
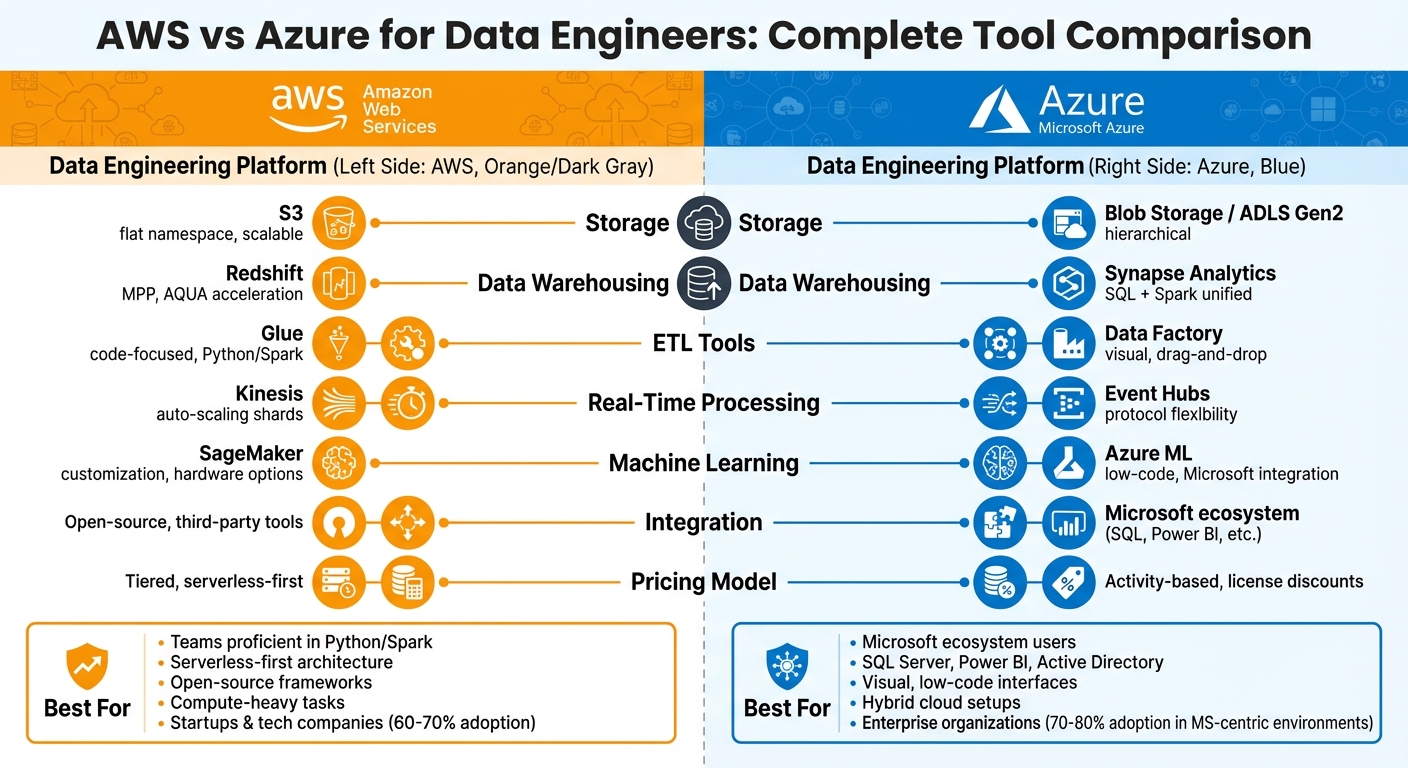
AWS vs Azure for Data Engineers: Tool Comparison
Choosing between AWS and Azure for data engineering depends on your organization's needs, existing tools, and team expertise. Here's a quick breakdown:
- AWS: Ideal for teams proficient in Python/Spark, focusing on serverless tools, open-source frameworks, and compute-heavy tasks. Key tools include AWS Glue, Redshift, and S3.
- Azure: Best for organizations already using Microsoft tools like SQL Server, Power BI, and Active Directory. Azure Data Factory and Synapse Analytics offer strong integration and a user-friendly, visual interface.
Quick Comparison
| Category | AWS | Azure |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | S3 (flat namespace, scalable) | Blob Storage / ADLS Gen2 (hierarchical) |
| Data Warehousing | Redshift (MPP, AQUA acceleration) | Synapse Analytics (SQL + Spark unified) |
| ETL Tools | Glue (code-focused, Python/Spark) | Data Factory (visual, drag-and-drop) |
| Real-Time Processing | Kinesis (auto-scaling shards) | Event Hubs (protocol flexibility) |
| Machine Learning | SageMaker (customization, hardware options) | Azure ML (low-code, Microsoft integration) |
| Integration | Open-source, third-party tools | Microsoft ecosystem (SQL, Power BI, etc.) |
| Pricing | Tiered, serverless-first | Activity-based, discounts for licenses |
Both platforms are powerful for data engineering. AWS offers flexibility and serverless scaling, while Azure excels in enterprise integration and hybrid setups. Pick the platform that aligns with your team’s skills and your existing infrastructure.
AWS vs Azure Data Engineering Tools Comparison Chart
AWS vs. Azure: Data Engineering Comparison and Best Practices | AWS | AZURE | KSR DATAVIZON
Data Storage and Processing Services
Getting data engineering right starts with dependable storage and processing solutions, and both AWS and Azure offer options that can handle complex workflows. AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage form the backbone of their respective ecosystems for data lakes, while Amazon Redshift and Azure Synapse Analytics manage large-scale analytics. The main distinction lies in how these platforms integrate with their ecosystems and handle the separation of compute and storage.
AWS S3 vs Azure Blob Storage
AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage are designed for scalable object storage, with compute and storage decoupled. AWS S3 integrates smoothly with tools like AWS Glue for ETL tasks, Amazon Athena for serverless querying, and Redshift Spectrum for data warehousing. On the other hand, Azure Blob Storage works natively with Azure Synapse Analytics, Power BI, and Azure Data Factory.
One major architectural difference is how they handle file organization. AWS S3 uses a flat namespace with folder-like prefixes, while Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen2 offers a hierarchical namespace. This structure allows for faster renaming and supports directory-level operations, making it easier for engineers accustomed to on-premises systems.
When it comes to access control, AWS uses IAM roles and bucket policies, whereas Azure takes a more layered approach with storage firewalls, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), and Shared Access Signatures (SAS). Both platforms support open data formats like Parquet, ORC, JSON, and CSV. Additionally, AWS S3 supports advanced frameworks like Apache Iceberg, Apache Hudi, and Delta Lake for transactional consistency.
| Feature | AWS S3 | Azure Blob Storage / ADLS Gen2 |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Virtually unlimited | Virtually unlimited |
| Storage Structure | Flat namespace with prefixes | Hierarchical namespace |
| Infrequent Access Tier | S3 Standard-IA | Cool Blob Storage |
| Archive Tier | S3 Glacier / Deep Archive (180+ days) | Archive Blob Storage (180+ days) |
| Access Control | IAM Roles, Bucket Policies | RBAC, SAS, Storage Firewall |
| Redundancy | LRS, ZRS, Cross-Region Replication | LRS, ZRS, GRS, GZRS |
| Key Integrations | Glue, Athena, EMR, Redshift Spectrum | Synapse Analytics, Data Factory, Power BI |
Both services offer tiered pricing models, with higher costs for immediate access and lower fees for infrequent or archival storage.
Next, let’s dive into how these platforms compare when it comes to data warehousing.
AWS Redshift vs Azure Synapse Analytics
Amazon Redshift is a cluster-based data warehouse optimized for analytical workloads, while Azure Synapse Analytics combines data warehousing, Apache Spark processing, and data management into a unified platform.
Redshift uses Advanced Query Accelerator (AQUA) to enhance query performance, claiming speeds up to 10× faster. AWS also states that Redshift delivers up to 3× better price-performance and 7× higher throughput compared to other cloud data warehouses. In contrast, Azure Synapse offers a comprehensive workspace - Synapse Studio - that supports data preparation, management, and visualization, along with over 95 pre-built connectors.
Synapse provides detailed access controls at schema, table, view, and column levels, while Redshift primarily manages access at the table level. For streaming data, Redshift integrates with Amazon Kinesis and MSK for near real-time analytics. Synapse achieves similar functionality through Apache Spark streaming.
| Feature | Amazon Redshift | Azure Synapse Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Cluster-based (MPP) with Serverless option | Unified (SQL + Spark) with Serverless option |
| Compute/Storage | Coupled in some nodes; separated in RA3 | Separated (scale independently) |
| Big Data Support | Redshift Spectrum (queries data in S3) | Native Apache Spark pools |
| Query Acceleration | AQUA (hardware-accelerated cache) | Result-set caching and materialized views |
| Authentication | AWS Directory Service (IAM) | Azure Active Directory (OAuth 2.0 support) |
| On-Demand Pricing | Starts at $0.25/hour for dc2.large nodes | Starts at $1.51/hour for DW100c |
| Serverless Pricing | ~ $3/hour of compute capacity | $5.65 per TB of data processed |
When it comes to pricing, both platforms offer flexible models tailored to their architectures. Redshift on-demand pricing starts at $0.25/hour for dc2.large nodes, with RA3 nodes ranging from $1.09/hour to $13.04/hour. Azure Synapse's dedicated SQL pools range from $1.51/hour to $453/hour, while serverless SQL costs about $5.65 per TB of data processed. Azure also provides up to 28% savings through reserved capacity with Synapse Commit Units.
Redshift is better suited for datasets over 100 GB and is not ideal for OLTP workloads or storing large binary objects directly. If you need a platform that integrates SQL and Spark seamlessly, Synapse’s unified tools can simplify your data engineering processes.
Data Integration and ETL Tools
Transferring and transforming data for analysis often requires ETL tools, and AWS Glue and Azure Data Factory offer two distinct methods. Glue leans on a code-driven approach, while Data Factory emphasizes a visual, drag-and-drop design. Your choice boils down to whether you prefer scripting or a more visual pipeline-building experience.
AWS Glue vs Azure Data Factory
AWS Glue is ideal for teams comfortable with coding in Python or Scala. It operates on Apache Spark and scales automatically without requiring manual setup. The transformation logic is written as code, giving users fine-tuned control over data operations. Glue Crawlers simplify schema management by automatically detecting and adding them to the Data Catalog, with the first 1 million objects included at no cost.
Azure Data Factory, on the other hand, offers a visual interface that caters to both technical and non-technical users. Its drag-and-drop design eliminates the need for coding. With over 90 built-in connectors, it supports SaaS and on-premises systems alike. Additionally, Data Factory can natively run SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packages, while Glue requires these packages to be converted or rewritten.
The two platforms also differ in how they manage workloads. AWS Glue is fully serverless, scaling resources automatically based on demand. Azure Data Factory relies on Integration Runtimes, which provide manual control over execution environments - making it a strong choice for hybrid setups that bridge cloud and on-premises systems. For orchestration, Data Factory offers advanced features like branching, loops, and conditional execution. Glue, meanwhile, provides basic job scheduling and dependency management, with more complex workflows typically handled through AWS Step Functions or Amazon Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (MWAA). Both platforms also support managed Apache Airflow for orchestrating complex workflows.
| Feature | AWS Glue | Azure Data Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Interface | Code-centric (Python, Scala) | Visual drag-and-drop |
| Scaling | Automatic serverless scaling | Configurable via Integration Runtimes |
| Connectors | 60+ (AWS-focused) | 90+ (Hybrid and multi-cloud) |
| Transformation Style | Script-based (Spark/Ray) | Visual Mapping Data Flows |
| SSIS Support | Requires package conversion | Native execution of SSIS packages |
| Pricing | $0.44 per DPU-hour (Spark jobs) | $0.10 per Azure IR vCore-hour (data movement) |
When it comes to pricing, AWS Glue charges $0.44 per DPU-hour for Spark jobs and $0.22 per Python shell jobs. Azure Data Factory uses an activity-based pricing model: data movement starts at $0.10 per Azure IR vCore-hour, while Data Flow execution begins at $0.274 per vCore-hour. Pipeline orchestration costs $0.001 per activity run after the first 2,000 monthly runs. Azure also offers a free tier that includes 5 data movement activities and 200 pipeline activities per month.
Apache Airflow on AWS and Azure
Both AWS and Azure extend their ETL capabilities with managed Apache Airflow for advanced workflow orchestration. Amazon Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (MWAA) integrates seamlessly with services like Glue, S3, and Redshift, with pricing based on the size of the environment and the number of workers. Azure offers similar managed Airflow capabilities but integrates them directly within the Azure Data Factory environment, allowing users to manage orchestration and data pipelines in a unified workspace.
Machine Learning and AI Tools
Incorporating machine learning into data pipelines is now more accessible thanks to platforms that prioritize both flexibility and seamless integration. For instance, AWS SageMaker offers extensive customization options along with specialized hardware, while Azure Machine Learning focuses on low-code tools and deep integration within Microsoft's ecosystem. This sets the stage for a closer comparison of these two platforms.
AWS SageMaker vs Azure Machine Learning
AWS SageMaker connects to data workflows using AWS Glue, whereas Azure Machine Learning integrates data pipelines through Azure Data Factory and Microsoft Fabric. These tools allow for direct execution of transformations within Azure's ecosystem. Choosing the right tool plays a critical role in optimizing your data pipeline and ensuring smooth operations.
According to Microsoft Documentation:
"Fabric provides an all-in-one platform that unifies the data and AI services required for modern analytics solutions... This approach contrasts with the AWS approach, where you often use separate services and must invest more effort in integration."
Both platforms support popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. AWS SageMaker goes a step further by offering native support for Apache MXNet and specialized hardware like AWS Trainium and Inferentia2, which are designed for efficient large-scale model training. On the other hand, Azure Machine Learning integrates seamlessly with tools like Power BI and Synapse, making it an attractive option for teams already embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem.
When it comes to automation, SageMaker Autopilot handles preprocessing and algorithm selection automatically. Meanwhile, Azure AutoML provides a user-friendly drag-and-drop Designer for building models with minimal effort. Real-world applications highlight their strengths: Airbnb relies on SageMaker for real-time pricing and personalized recommendations, while Volkswagen uses Azure Machine Learning to develop predictive maintenance models that enhance manufacturing efficiency and reduce downtime.
Here’s a quick comparison of features between AWS SageMaker and Azure Machine Learning:
| Feature | AWS SageMaker | Azure Machine Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Primary ETL Partner | AWS Glue (Glue Studio) | Azure Data Factory / Microsoft Fabric |
| Framework Support | TensorFlow, PyTorch, MXNet, Apache Ray | TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn, ONNX |
| Automation Tool | SageMaker Autopilot | Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) |
| Development IDE | SageMaker Studio | Azure Machine Learning Studio (Designer) |
| Specialized Hardware | Trainium, Inferentia2, P5 (NVIDIA H100) | N-Series GPUs, Virtual Machine Scale Sets |
| Deployment | SageMaker Endpoints, AWS Lambda | Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), Azure Functions |
Both platforms follow a pay-as-you-go pricing model. AWS SageMaker offers a free tier that includes 250 hours of m5.xlarge notebook usage per month for the first two months. Similarly, Azure Machine Learning provides 30 hours of computing per month on basic instances. For ETL work, AWS Glue charges $0.44 per Data Processing Unit (DPU) hour, while Azure Data Factory uses activity-based pricing and includes a $200 credit for the first 30 days, along with five low-frequency activities always free.
sbb-itb-61a6e59
Real-Time Data Processing and Streaming
When it comes to real-time data processing, AWS and Azure stand out with their ability to handle millions of events per second. However, they take different approaches when it comes to scaling, protocol compatibility, and integration with analytics tools. Let’s dive deeper into how their offerings compare.
AWS Kinesis vs Azure Event Hubs and Stream Analytics
For real-time data ingestion, AWS Kinesis Data Streams and Azure Event Hubs are the go-to solutions on each platform. The key difference lies in protocol support. While Kinesis relies on HTTPS, Azure Event Hubs supports multiple protocols like AMQP, Apache Kafka, and HTTPS. This makes Azure an appealing option for teams already using Kafka pipelines, as they can integrate without rewriting code.
Scaling also highlights their differences. AWS Kinesis On-Demand mode dynamically adjusts shard counts, allowing up to 200 MB/s for writes and 400 MB/s for reads by default. On the other hand, Azure Event Hubs uses an "Auto-inflate" feature to increase Throughput Units (TUs) as traffic spikes, but it doesn’t scale down automatically. This means users must manually reduce TUs after peak activity to avoid extra costs.
When it comes to analytics, Azure pairs Event Hubs with Stream Analytics, a SQL-based tool designed for straightforward real-time tasks. It guarantees 99.9% availability and ensures exactly-once event processing. AWS, on the other hand, integrates Kinesis with Managed Service for Apache Flink (formerly Kinesis Data Analytics), which supports both SQL and Flink for more advanced processing. For Spark-based workflows, AWS Glue Streaming offers a visual interface through Glue Studio, making it easier for engineers familiar with Spark to build ETL pipelines.
Here’s a side-by-side look at their key streaming features:
| Feature | AWS Kinesis Data Streams | Azure Event Hubs |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Unit | Shards | Partitions (within Namespaces) |
| Scaling | Auto-scales up and down (On-Demand mode) | Auto-scales up; manual scale down |
| Protocol Support | HTTPS | AMQP, Apache Kafka, HTTPS |
| Max Retention | 365 days | 90 days (Premium/Dedicated) |
| Analytics Tool | Managed Service for Apache Flink | Azure Stream Analytics |
| Delivery Guarantee | At-least-once (standard) | Exactly-once processing |
| Consumer Throughput | Enhanced Fan-Out (2 MB/s per consumer) | Consumer Groups (shared throughput) |
Pricing Models
Pricing structures further set these platforms apart. AWS Kinesis offers two modes: On-Demand, which charges per GB of data ingested and retrieved along with an hourly stream fee, and Provisioned, which bills based on the number of shards and records written. Meanwhile, Azure Event Hubs uses tiered pricing (Basic, Standard, Premium, Dedicated), with Throughput Units billed hourly and additional costs for ingress events. For analytics, Azure Stream Analytics charges based on the number of Streaming Units consumed.
Both platforms offer powerful tools for real-time streaming, but your choice will likely depend on your existing infrastructure, protocol requirements, and cost considerations.
Enterprise Integration and Ecosystem Fit
When choosing a platform for your data engineering workflow, integration with your existing tools can be a deciding factor. Azure stands out in Microsoft-centric environments, with adoption rates of 70–80% among organizations deeply invested in Active Directory, Microsoft 365, Power BI, and SQL Server. Its tight integration with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) simplifies identity management. AgileSoftLabs highlights this advantage:
Azure wins decisively for enterprise identity scenarios. If your organisation uses Active Directory, Azure's native integration eliminates significant complexity.
This sets the stage for understanding how these platforms align within enterprise and hybrid environments.
Azure and the Microsoft Ecosystem
Azure’s strength lies in its seamless integration with Microsoft’s enterprise tools. For teams already using SQL Server, Power BI, and Office 365, Azure Data Factory enhances workflows with over 90 built-in connectors. The Azure Hybrid Benefit offers cost savings by allowing organizations to reuse existing on-premises licenses, cutting Windows VM costs by 40–80% and SQL Server costs by 55–80%. Additionally, for those migrating legacy SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packages, Azure Data Factory supports native cloud execution, which can reduce costs by up to 88%. Its Self-hosted Integration Runtime ensures secure data transfers between on-premises systems and Azure, making hybrid cloud setups more manageable.
AWS and Third-Party Integration
AWS, on the other hand, focuses on flexibility and compatibility with third-party tools. This open architecture appeals to startups and tech-savvy companies, with adoption rates of 60–70% in these sectors, thanks to its developer ecosystem and extensive documentation. AWS Glue connects to over 100 data sources, while services like Direct Connect and PrivateLink enable secure communication with third-party systems - features particularly valued in industries like finance and government. However, AWS IAM requires more effort to integrate with on-premises Active Directory compared to Azure’s seamless approach. AWS excels when working with tools like Snowflake, Databricks, or MongoDB, leveraging its open architecture and extensive API support. Notably, over 60% of Azure VMs run Linux, showing that both platforms can adapt beyond their core ecosystems.
| Feature | AWS Integration Approach | Azure Integration Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Ecosystem | Third-party, Open Source, Startups | Microsoft Enterprise (M365, SQL Server, AD) |
| Identity Management | AWS IAM (requires federation setup) | Native Azure AD / Entra ID (seamless) |
| Hybrid Access | Direct Connect, VMware Cloud on AWS | ExpressRoute, Azure Hybrid Benefit |
| Data Connectors | 100+ (JDBC, AWS ecosystem focus) | Aligns with diverse enterprise systems |
| Legacy ETL Support | Manual rewrite to Python/Scala | Native SSIS package execution |
Ultimately, the best platform is the one your team can use effectively. As AgileSoftLabs notes:
The platform your team can operate confidently and efficiently beats the technically 'better' platform every single time.
If your organization relies heavily on Microsoft tools, Azure’s native integrations can save time and reduce costs. On the flip side, if flexibility with third-party tools and open-source frameworks is a priority, AWS offers the ecosystem and resources to meet those needs.
Performance, Scalability, and Costs
Elasticity and Processing Speed
When it comes to compute benchmarks, AWS takes the lead, thanks to its Graviton processors, which deliver up to 40% better price-performance ratios. Independent studies show AWS outperforming in seven out of ten categories for CPU and memory performance. This makes AWS a strong choice for compute-heavy tasks like large-scale ETL jobs or training machine learning models.
On the other hand, Azure shines in random read/write operations, achieving 27.53 MB/s for 4K operations, while AWS dominates in sequential writes, reaching 46.25 MB/s. This makes Azure better suited for tasks like database operations, whereas AWS is ideal for bulk data transfers or log ingestion. For data warehousing, Amazon Redshift employs massive parallel processing (MPP) with elastic scaling to handle fluctuating workloads. Meanwhile, Azure Synapse Analytics offers a unified environment that’s particularly appealing to organizations already using Microsoft tools. Azure also claims its SQL Managed Instance runs up to five times faster than AWS RDS for critical workloads, with SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines performing up to 57% faster than its AWS EC2 counterpart.
In terms of scalability, AWS Glue adjusts serverlessly, dynamically scaling workers to meet demand. In contrast, Azure Data Factory requires manual configurations through Integration Runtimes. As Ott Salmar, Co-Founder of Hykell, puts it:
AWS is the clear winner for compute-intensive tasks and AI/ML... Azure remains the path of least resistance for organizations deeply embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem.
This performance advantage directly impacts cost efficiency, which we’ll explore next.
Pricing Models and Total Ownership Costs
The efficiency of each platform's hardware not only affects performance but also plays a big role in shaping pricing and overall costs. Both AWS and Azure use pay-as-you-go pricing, but their approaches differ. AWS offers granular, tiered pricing, where costs decrease as usage increases - like how S3 storage becomes cheaper per GB as you store more data. Azure, on the other hand, leans heavily on ecosystem discounts, such as the Hybrid Benefit, which can save up to 85% on pay-as-you-go pricing when you bring your own Microsoft licenses. For Windows-based workloads, Azure often proves more economical, with AWS Windows instances costing as much as five times more.
AWS Glue follows a tiered pricing model, while Azure Data Factory charges based on activities, including pipeline runs and data movement. Both platforms reward long-term commitments: AWS Savings Plans and Azure Reserved VM Instances can cut costs by up to 72%. For workloads that can handle interruptions, spot instances on both platforms can slash compute costs by as much as 90%.
However, data egress costs can significantly add to your expenses. While inbound data transfers are free on both platforms, outbound transfers differ. Azure provides the first 100GB of internet egress free each month, while AWS charges about $0.01 per GB for cross-region transfers. Storage tiers also play a role in cost management - archiving older data to AWS S3 Glacier or Azure Archive Blob can reduce storage expenses by over 90% compared to standard tiers.
| Service Category | AWS Pricing | Azure Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Object Storage | S3 Standard: ~$0.023/GB/month | Blob Storage (Hot): ~$0.018/GB/month |
| Serverless Compute | Lambda: $0.20 per 1M requests | Functions: First 1M requests free |
| ETL/Integration | Glue: $0.44 per DPU-Hour | Data Factory: Activity-based billing |
| Long-term Discounts | Savings Plans: Up to 72% off | Reserved Instances: Up to 72% off |
| License Reuse | Not available | Hybrid Benefit: Up to 85% off |
Ultimately, the cost-effectiveness of each platform depends on your workload and existing infrastructure. If you're heavily invested in Microsoft licenses, Azure's Hybrid Benefit can offer substantial savings. For compute-heavy tasks that require flexible scaling, AWS Glue’s serverless model and Graviton processors often provide better value. Before locking in any reservations, tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Azure Advisor can help you identify over-provisioned resources and optimize your setup. Balancing both performance and pricing will guide you to the solution that best fits your data engineering needs.
Conclusion: Picking the Right Platform
Deciding between AWS and Azure isn't about identifying the "better" platform - it’s about finding the one that aligns with your needs. The choice boils down to three main factors: your existing infrastructure, your team’s skills, and the specific requirements of your projects.
If your organization heavily relies on Microsoft tools like Power BI, SQL Server, or Office 365, Azure might feel like a natural extension. Its Data Factory offers a user-friendly, low-code interface that simplifies deployment, even without deep Spark expertise. Azure also shines in hybrid setups, enabling secure data movement between on-premises systems and the cloud through its Self-hosted Integration Runtime. As Zach Wilson aptly puts it:
Pick Azure if you're all-in on M365/Power BI/Azure AD and want a unified, governed experience. Pick AWS if you want serverless-first, open table formats (Iceberg/Delta), and polyglot flexibility.
On the other hand, AWS is a strong contender for compute-heavy, script-driven data engineering tasks. If your team is proficient in Python or Spark and you're building large-scale data lakes with tools like S3, Redshift, and Athena, AWS Glue’s serverless design and auto-scaling capabilities can be a game-changer. AWS also stands out for its serverless-first approach, support for open table formats, and flexibility for diverse programming needs, making it a favorite among tech startups and innovation-driven teams.
Ultimately, start with what you know. If your organization is already rooted in AWS, leverage Glue and Redshift. If you’re more Microsoft-centric, tap into Data Factory and Synapse. Core skills like SQL, Python, and ETL logic are transferable, so you’re not locked into one platform forever. Both AWS and Azure provide powerful tools for data engineering - choose the one that best fits your team’s expertise and your organization’s foundation.
FAQs
What are the main differences between AWS Glue and Azure Data Factory for ETL workflows?
AWS Glue and Azure Data Factory are both excellent options for managing ETL workflows, but they shine in slightly different areas. AWS Glue is a serverless ETL service tailored for the AWS ecosystem. It simplifies tasks like schema discovery, data cataloging, and large-scale data processing, making it a strong choice for projects centered around AWS services.
In contrast, Azure Data Factory is a highly adaptable data integration platform. It supports a wide array of data sources, including hybrid and multi-cloud setups. With its intuitive interface, it handles complex workflows, from batch processing to real-time streaming, and diverse data pipelines with ease.
If your focus is on seamless AWS integration and automated serverless workflows, AWS Glue is a great fit. However, for handling data from multiple environments and orchestrating complex pipelines, Azure Data Factory offers the flexibility you need.
What are the key differences between AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage for file organization and access control?
AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage are powerful cloud object storage solutions, but they handle file organization and access control differently.
In AWS S3, data is stored in buckets, with objects placed inside these buckets. Permissions are highly flexible, managed through a combination of IAM policies, bucket policies, and ACLs, allowing for detailed control. Meanwhile, Azure Blob Storage organizes data into containers within storage accounts. It relies on role-based access control (RBAC) and shared access signatures (SAS) to manage permissions, tightly integrating with Azure's overall ecosystem.
Both services offer encryption and compliance tools to keep data secure. AWS S3 stands out with its advanced and customizable policy options, while Azure Blob Storage focuses on smooth integration with other Azure services, simplifying permission management within its ecosystem.
Which platform is better for integrating with Microsoft tools: AWS or Azure?
Azure stands out as the top option for businesses deeply rooted in the Microsoft ecosystem. Being a part of this ecosystem, it works effortlessly with tools like Windows Server, Active Directory, and other Microsoft enterprise services. This makes Azure an excellent fit for organizations already relying on Microsoft technologies, as it ensures smooth and efficient integration.
On the other hand, AWS is known for its versatility and platform-neutral approach. However, it doesn’t offer the same depth of native integration with Microsoft-specific tools. For companies that prioritize seamless compatibility with Microsoft products, Azure is the better choice.
