
Data Engineering Portfolio: 5 Projects That Get Hired
Want to land a data engineering job? Build a portfolio that proves you can deliver. This article highlights five key projects that hiring managers value most, covering skills like real-time streaming, ETL workflows, data modeling, and observability. Each project demonstrates expertise with tools like Kafka, Snowflake, Airflow, and AWS, while focusing on solving real-world data challenges. Here's a quick breakdown:
- Real-Time Streaming with Kafka & Snowflake: Build pipelines for high-throughput data processing and visualization.
- ETL with Airflow & Databricks: Orchestrate workflows and process large datasets efficiently.
- Data Warehouse with Snowflake & dbt: Design ELT pipelines for scalable analytics.
- Data Lake on AWS S3 & Redshift: Create lakehouse architectures for petabyte-scale analytics.
- Pipeline with Observability (PySpark & Monte Carlo): Ensure data quality and reliability for production systems.
Each project emphasizes end-to-end implementation, cost optimization, and industry-standard practices. These are the skills that set you apart in a competitive job market, especially as AI-driven systems demand clean, reliable data pipelines.
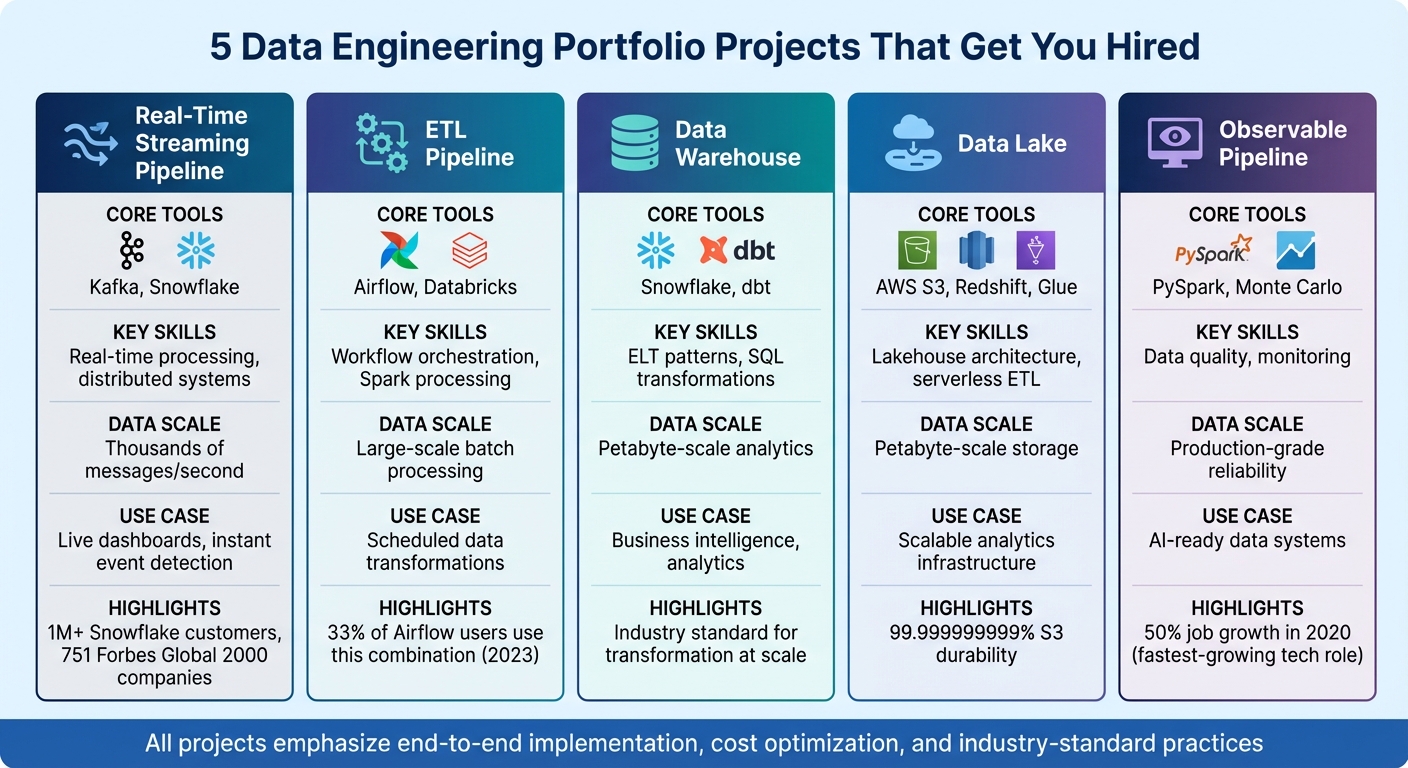
5 Essential Data Engineering Portfolio Projects Comparison
1. Real-Time Streaming Pipeline with Kafka and Snowflake
Mastering Key Tools and Technologies
Creating a real-time streaming pipeline using Apache Kafka and Snowflake highlights your expertise with cutting-edge data infrastructure tools. As Mark Smallcombe, CTO at Integrate.io, puts it:
Apache Kafka has emerged as the leading open-source stream-processing software... capable of seamlessly handling thousands of messages per second.
This kind of project demonstrates your ability to work with distributed systems that prioritize high throughput and fault tolerance - essential skills in managing data streams for AI models. Snowflake, with its architecture that separates storage from compute, allows independent scaling of resources. It’s a powerhouse capable of managing petabytes of data for over 1 million customers, including 751 companies from the Forbes Global 2000. Snowflake’s VARIANT data type also enables you to ingest raw JSON data from Kafka streams without heavy pre-processing, showcasing your ability to handle semi-structured data efficiently. These skills form the backbone of building practical, end-to-end data pipelines.
Demonstrating Full Project Implementation
A real-time data pipeline involves more than just moving data - it’s about transforming and visualizing it effectively. Start by developing Python producers to fetch real-time data from APIs, such as weather or transit feeds, and publish this data to Kafka topics. Deploy a Kafka-Zookeeper cluster using Docker to highlight your DevOps expertise. From there, integrate Kafka with Snowflake using tools like the Snowflake Kafka Connector or Snowpipe for automated data loading. Use Snowflake Streams and Tasks to automate SQL-based transformations. Finally, orchestrate the entire workflow with Apache Airflow and connect the results to Tableau or Streamlit for live dashboard visualizations.
This kind of project demonstrates your ability to manage the entire data lifecycle - from ingestion to transformation to visualization - making your portfolio stand out.
Tackling Challenges and Optimizing Solutions
Building pipelines isn’t just about moving data - it’s about solving complex challenges in distributed systems. For instance, managing consumer groups, handling network partitions, and optimizing Kafka partition counts are all critical to ensuring throughput and reliability. To show production readiness, incorporate monitoring tools like CloudWatch or Kafka-UI to track consumer lag and broker health.
Cost control is another key aspect. Use Snowflake’s AUTO_SUSPEND and AUTO_RESUME features to ensure compute resources are only active when needed. Organize your data systematically using the Medallion Architecture - Bronze for raw data, Silver for cleansed data, and Gold for business-ready insights. These optimizations not only enhance performance but also demonstrate your ability to deliver scalable and efficient solutions.
Meeting Industry Standards
This pipeline design aligns with real-world workflows used by leading companies. Real-time processing is critical for identifying issues like service outages or checkout failures as they happen, rather than discovering them hours later through batch reports. As Khushbu Shah from ProjectPro notes:
Mastering Snowflake isn't just about running queries, but it's about designing end-to-end data pipelines, managing raw and semi-structured data, and delivering real-time insights.
With Snowflake boasting a net revenue retention rate of 125% and serving as the backbone for AI-driven products, this project proves your ability to build reliable systems. These systems ensure clean, up-to-date data, preventing AI errors caused by outdated or messy inputs.
2. ETL Pipeline with Airflow and Databricks
Mastering Tools That Are Shaping the Industry
Building an ETL pipeline using Apache Airflow and Databricks is a powerful way to showcase your technical expertise. In fact, 33% of respondents in the 2023 Airflow survey reported using this combination. This setup highlights your ability to manage intricate workflows and handle large-scale data processing. Airflow takes care of scheduling, handling dependencies, and retrying tasks in case of temporary failures, while Databricks provides a high-performance environment for Spark-based data transformations through its notebooks.
Thanks to the Databricks Airflow provider package, orchestrating tasks is simplified to just a few lines of DAG code. Operators like DatabricksCopyIntoOperator make it easy to load data from AWS S3, and DatabricksNotebookOperator allows you to execute transformation logic seamlessly. As Tamara Fingerlin, Senior Developer Advocate at Astronomer, explains:
Implementing [ETL/ELT] operations are the fundamental patterns in data engineering and implementing them is often the first task for beginner data engineers to work on.
This combination of tools equips you to build pipelines that are not only functional but also ready for real-world deployment.
Building Complete, Real-World Pipelines
Start by storing raw data in AWS S3 and setting up Airflow connections like databricks_default and aws_default with the necessary access tokens. Use the DatabricksCopyIntoOperator to load this data into Databricks Delta tables. This operator supports various data formats and can handle schema evolution efficiently. Create modular Databricks Notebooks to clean, transform, and visualize the data, and orchestrate these workflows with Airflow DAGs.
To keep things organized, store your SQL queries in an include folder and import them into your DAGs. Add data quality checks using operators like SQLColumnCheckOperator to ensure data integrity. If issues are detected, you can halt the pipeline or trigger alerts through tools like Slack. This modular and production-ready setup demonstrates your ability to handle complex data workflows from start to finish.
Solving Problems and Optimizing Performance
You can also showcase your optimization skills by making your pipeline more cost-efficient. For instance, use a DatabricksWorkflowTaskGroup to run multiple notebooks as a single Databricks Job, which benefits from lower "Workflows" compute rates compared to standard interactive clusters. Parallelize the processing of multiple S3 files with Dynamic Task Mapping, and implement incremental processing to cut down on compute time and costs. Additionally, by configuring a job_cluster_key within your workflow task group, you can reuse clusters across tasks, reducing overhead and improving efficiency.
These optimizations not only reduce costs but also enhance system performance - skills that are highly valued by employers.
3. Data Warehouse on Snowflake with dbt Modeling
Proficiency with Essential Tools and Technologies
Building an ELT pipeline using Snowflake and dbt showcases your expertise in modern data engineering. This project adopts the ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) pattern, where raw data is first loaded into Snowflake, and all transformations occur directly within the warehouse using dbt. As Shreyas Karle, a Data Analytics & Engineering Professional, puts it:
Modern warehouses like Snowflake make it cheaper and faster to do the transformations after loading.
By relying on Snowflake's parallel processing capabilities, this method eliminates the need for external compute resources. You'll demonstrate mastery in SQL-based transformations, version control with Git, and automated testing - skills that are highly valued by hiring managers. Additionally, you'll secure your environment and streamline version control to ensure efficient management of transformations.
End-to-End Project Implementation
This project involves setting up Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in Snowflake, integrating dbt with Git, and building a three-layer transformation architecture: staging, intermediate, and mart models.
- Staging models (materialized as views) focus on cleaning and standardizing raw data.
- Intermediate models handle complex joins and business logic.
- Mart or fact tables (materialized as tables) aggregate data into actionable metrics for business intelligence tools.
With the architecture in place, you'll also focus on optimizing performance and managing costs effectively.
Problem-Solving and Optimization in Action
This project emphasizes performance tuning and cost efficiency. You'll learn how to materialize models strategically, apply incremental updates for large datasets, and enforce data quality using dbt's built-in and custom tests. Additionally, you'll create custom macros for query tagging and cost tracking in Snowflake. As Luis Leon from dbt Labs explains:
dbt is the industry standard for data transformation at scale. It's a framework that sits on top of your data warehouse and lets anybody who can write SQL statements deploy production-grade pipelines on top of Snowflake.
By implementing these techniques, you’ll demonstrate your ability to solve complex problems while maintaining efficiency.
Adherence to Industry Best Practices
This project mirrors analytics engineering best practices by incorporating reusable macros and automated documentation with dbt docs generate. These tools ensure your pipelines are transparent and easy to maintain. Using orchestration tools like Apache Airflow or Snowflake Tasks, you can automate dbt runs and ensure downstream processes only execute after passing tests. This approach highlights how robust and efficient pipelines are essential to standing out in today’s competitive job market. By combining declarative infrastructure, automated testing, and self-documenting pipelines, you'll align your work with the workflows of top-tier data teams.
4. Data Lake on AWS S3 and Redshift
Demonstrates Proficiency with In-Demand Tools and Technologies
Including a data lake project in your portfolio highlights your ability to create scalable analytics infrastructure - a key skill for today’s data engineers. By leveraging Amazon S3's impressive 99.999999999% durability alongside tools like AWS Glue for serverless ETL, Lake Formation for access control, and Lambda for event automation, you can implement a Lakehouse architecture capable of handling petabyte-scale analytics. This project showcases your expertise in integrating S3 and Redshift using high-throughput commands like COPY and UNLOAD.
You’ll also use the AWS Glue Data Catalog to centralize metadata and AWS Lambda for event-driven automation. As Farah Abdirahman puts it:
The data engineer acts as the bridge, ensuring that raw data from logs, APIs, and third-party sources becomes analytics-ready for everyone else.
This architecture ensures a smooth and automated data flow, proving your ability to build systems that scale efficiently.
Showcases End-to-End Project Implementation Capabilities
This project walks through the complete lifecycle of a data lake. Raw data is ingested into an S3 "raw zone", where AWS Glue Crawlers infer schemas and update the Data Catalog. Next, you’ll write PySpark scripts in AWS Glue to clean, deduplicate, and partition the data by date (year/month/day/hour), converting it into Parquet format for the "processed zone". The processed data is then loaded into Redshift using the COPY command, while Redshift Spectrum enables direct querying of Parquet files stored in S3.
Automation is a key focus here. For example, an S3 PutObject event can trigger a Lambda function to start a Glue job. Security is also prioritized, with IAM roles and AWS Secrets Manager safeguarding credentials. This comprehensive workflow demonstrates your ability to handle all aspects of data lake development, from ingestion to transformation and storage.
Highlights Problem-Solving and Optimization Skills
This project emphasizes performance optimization, a critical skill for data engineers. Partitioning strategies combined with pushdown predicates ensure that queries avoid scanning entire S3 buckets, significantly reducing both query times and costs. Converting raw data into Parquet format not only lowers storage expenses but also speeds up columnar reads in tools like Athena and Redshift.
For large datasets, you’ll implement incremental ETL workflows using Change Data Capture (CDC) and upsert patterns in Redshift, ensuring that only new or updated records are processed. Managing complex pipelines becomes scalable with AWS Glue blueprints, which separate ETL logic from job definitions. This allows for programmatic deployment using JSON configuration files. As Moustafa Mahmoud, Solutions Architect at AWS, explains:
AWS Glue blueprints allow data engineers to build and maintain AWS Glue jobs landing data from RDBMS to your data lake at scale.
These optimization strategies reflect industry best practices, making your project stand out to hiring managers.
Aligns with Industry-Standard Practices and Workflows
This architecture is built around the Medallion pattern, which organizes data into Bronze (raw), Silver (cleansed), and Gold (business-ready) layers - a widely adopted framework in data engineering. By decoupling storage (S3) from compute (Redshift/Glue), you demonstrate how companies can scale storage without inflating processing costs. Centralized metadata management through the Glue Data Catalog ensures that S3 data is always searchable and ready for querying, which is invaluable for analytics teams.
This setup also supports AI and machine learning workloads, as clean, partitioned data inputs reduce errors during model training. By mastering these AWS-based tools and workflows, you show that you’re ready to tackle real-world challenges, aligning with what hiring managers look for in top candidates.
5. Pipeline with Observability Using PySpark and Monte Carlo
Demonstrates Proficiency with In-Demand Tools and Technologies
Building a pipeline with PySpark and integrating Monte Carlo for observability reflects a major shift in how data engineering is approached today. PySpark has become a go-to tool for creating distributed ETL pipelines that can handle the chaotic nature of production data - think inconsistent formats, malformed records, and unexpected schema changes. By pairing PySpark with Monte Carlo, you're not just moving data from one place to another; you're ensuring that the data is clean, reliable, and ready to support AI systems that might serve tens of thousands - or even hundreds of thousands - of users. Observability is what makes it possible to deliver the kind of high-quality, partitioned data that modern AI-powered products depend on. This combination of tools signals a shift from simply processing data to actively ensuring its quality throughout the pipeline.
Showcases End-to-End Project Implementation Capabilities
This project walks you through creating a production-ready pipeline from scratch. A key part of this process is organizing your code effectively - for example, separating orchestration logic (e.g., in a main.py file) from ETL-specific modules (e.g., src/etl_pipeline.py). During the extract phase, define data schemas explicitly using tools like StructType and StructField instead of relying on automatic inference. This proactive approach helps catch data type issues early. Additionally, using Spark's PERMISSIVE mode ensures that malformed rows are flagged with null values instead of causing the entire job to fail.
The transformation phase focuses on cleaning and standardizing data in logical steps. For instance, you might normalize customer IDs, strip currency symbols from price fields, and standardize date formats using functions like coalesce() to handle variations. Instead of discarding records that look suspicious, add quality flag columns (e.g., CHECK_ZERO_PRICE) so anomalies can be reviewed without losing potentially valuable information. Once the data is loaded, run sanity checks using Spark SQL to verify metrics like record counts, date ranges, and anomalies. Automated summary reports - including metrics like total records processed, unique identifiers, and total revenue - help confirm that everything ran as expected. With the pipeline functioning reliably, you can then shift your focus to improving performance and building in robust error handling.
Highlights Problem-Solving and Optimization Skills
This project emphasizes a defensive approach to engineering by preparing for real-world data challenges. For instance, during the extraction phase, you can store incoming data as strings (StringType()) and only handle type conversion and error management during the transformation phase. Adding detailed logging with Python's logging module and wrapping your pipeline in try-except-finally blocks ensures that the Spark session closes properly, even if errors occur.
For scaling performance, avoid using memory-intensive methods like .toPandas(). Instead, rely on Spark's native output methods, such as df.write.parquet() or df.write.csv(), which are built to handle large datasets efficiently. Monte Carlo's observability layer adds another layer of reliability by tracking potential issues, like data downtime, freshness problems, unexpected volume changes, or schema mismatches. By incorporating proactive monitoring, this project goes beyond the basics, showing you can create a system that's ready for the demands of real-world production. These practices demonstrate your ability to tackle production-scale challenges and build systems that hiring managers can trust.
Aligns with Industry-Standard Practices and Workflows
In today's data-driven world, observability is a non-negotiable part of modern data infrastructure. Data engineering roles have been growing rapidly - in fact, they were the fastest-growing tech job in 2020, with a 50% increase, compared to just 10% for data science roles. Companies now expect pipelines to include built-in monitoring and alerting systems to ensure data accuracy and reliability, even under the pressure of processing high volumes of real-time data.
This project aligns perfectly with the Modern Data Stack philosophy, where observability tools manage the messy aspects of data before it ever reaches users or AI applications. By showing that your pipeline can detect anomalies, gracefully handle imperfect data, and maintain high quality at scale, you're proving to hiring managers that you can build the backbone of AI-first products.
sbb-itb-61a6e59
These Data Engineering Projects Give You An Unfair Advantage
Why These Projects Impress Hiring Managers
Your portfolio is more than just a showcase of your work - it's a strategic way to highlight your ability to tackle real-world data challenges. Hiring managers are looking for engineers who can build reliable, scalable pipelines that perform under pressure. This is especially important for AI-driven products, where unstable inputs can lead to system failures. The projects outlined in this article demonstrate your ability to design production-grade pipelines that are dependable, traceable, and scalable - key components for AI-ready systems.
These projects align perfectly with what companies need today. Modern data engineering requires real-time pipelines and flexible infrastructure to support the rapid evolution of AI applications, like Agentic AI and ChatGPT plugins. For example, businesses now expect engineers to use tools like Kafka and Snowpipe to enable instant event detection, rather than relying on outdated batch reporting methods that run once a day.
The technical skills showcased here directly match what employers are actively searching for. Consider Snowflake, a platform used by over 1 million customers, including 751 of the Forbes Global 2000 companies, with a net revenue retention rate of 125%. Demonstrating your expertise in Snowflake’s storage and compute separation, along with dbt’s modular transformations, signals your readiness to handle enterprise-scale operations. Similarly, showcasing PySpark’s capabilities for processing massive datasets proves you can efficiently manage resources when working with petabytes of data.
What truly stands out is the end-to-end ownership these projects demonstrate - something hiring managers highly value. Take, for instance, a production-grade pipeline implemented in April 2025, which utilized AWS EC2, Airflow, and Snowflake to automate the ingestion of Redfin real estate data. This pipeline powered business-ready dashboards in Google Looker Studio, providing automated insights into home price trends and inventory changes. This kind of automation delivers the business impact employers are looking for.
Moreover, these projects highlight your problem-solving expertise, which goes far beyond just writing code. By implementing idempotent tasks, creating quality gates with dbt tests, and organizing code into modular layers, you show that you can handle the critical preprocessing work that makes up 80% of analytics tasks. As Shreyas Karle, a Data Analytics & Engineering Professional, puts it:
Data engineering is no longer about just moving data. It's about making it reliable, traceable, and scalable - so analytics teams can focus on insights, not firefighting.
Your ability to anticipate challenges and consistently deliver actionable insights makes you an outstanding candidate for any data engineering role.
Build These Projects in DataExpert.io Academy Bootcamps
Once you've built production-ready projects, the next step is to truly master them through hands-on training. That's where DataExpert.io Academy comes in. Their specialized boot camps are designed to help you create advanced, real-world projects while gaining practical, job-ready skills. These aren't just basic tutorials - you'll dive into every aspect of the data engineering lifecycle, from data ingestion and storage to processing and visualization. Along the way, you'll work with over 30 industry-standard tools like Databricks, Snowflake, AWS, Kafka, and Airflow.
Every month, the academy rolls out four new projects. These programs are crafted and led by seasoned data engineers from FAANG companies, professionals with years of experience hiring, managing, and training data teams. This means you're learning directly from experts who know what employers are looking for. The result? You'll walk away with impressive, tangible projects to showcase in your portfolio.
When it comes to enrollment, you’ve got options. You can go for the All-Access Subscription at $125 per month or $1,500 per year, which gives you 250+ hours of content and full platform access. If you're looking for something more intensive, there’s the 5-week Winter 2026 Boot Camp for $3,000 or the 15-week Data and AI Engineering Challenge for $7,497 [website]. These programs include extras like guest speaker sessions, mentor support, and capstone projects, all designed to help you deliver end-to-end solutions.
But the benefits don’t stop at building projects. The academy also prepares you for the job search. You'll get tailored interview prep for SQL, Python, data modeling, and system design, plus one-on-one guidance for resume reviews and salary negotiations. With a Trustpilot rating of 4.6/5 and certifications to back up your skills, you'll have credentials that stand out. And considering that only 5% to 10% of job applicants typically present a portfolio during the hiring process, completing these projects gives you a clear edge. You'll be ready to show hiring managers that you're equipped with the production-level expertise they’re looking for.
Conclusion
A strong portfolio showcases your ability to design, build, and manage complete systems from start to finish. The five projects discussed here - real-time streaming with Kafka and Snowflake, ETL orchestration using Airflow and Databricks, data warehouse modeling with dbt, data lake architecture on AWS, and observability-driven pipelines - cover every stage of the data lifecycle, from ingestion to monitoring. These examples demonstrate your capacity to handle batch and streaming data while ensuring data quality, a vital skill for maintaining system reliability under demanding conditions.
Looking ahead to 2025-2026, hiring managers are placing a premium on engineers who can develop AI infrastructure that minimizes issues like hallucinations in LLMs caused by poor-quality data. Your portfolio must highlight production-ready pipelines that prevent such failures and support scalable, AI-driven solutions.
To get started, choose a project aligned with your ideal role. Use tools like Docker or GitHub Codespaces to ensure your setup is reproducible. Pull data from public repositories such as Kaggle or AWS Public Datasets, and create a detailed architecture diagram to illustrate your design approach before diving into the code. Build the pipeline end-to-end, integrate observability tools with data quality checks, and showcase your results through a live dashboard using platforms like Streamlit.
Once your pipeline is complete, document every step thoroughly. Write clear README files, comment your code, and explain the business problem your project addresses - not just the technical tools involved. This level of documentation highlights not only your technical expertise but also your ability to deliver production-ready solutions. When you can demonstrate that your systems can handle complex, large-scale data challenges, you’ll stand out to hiring managers. As Mike Shakhomirov puts it:
Data engineering projects you were involved in or responsible for are the ultimate compass that tells a recruiter about your experience, how good you are and why they should hire you.
FAQs
What skills can you showcase by building a real-time data pipeline with Kafka and Snowflake?
Building a real-time data pipeline with Apache Kafka and Snowflake is a great way to showcase essential data engineering skills. For starters, it highlights expertise in event-driven architecture. This includes designing Kafka topics, managing producers and consumers, ensuring reliable data delivery even in the face of failures, and scaling partitions to handle high throughput efficiently.
It also demonstrates the ability to integrate seamlessly with Snowflake’s cloud data warehouse. Tools like Snowpipe or Kafka connectors come into play here, enabling the ingestion of streaming data while keeping schemas consistent and up to date.
Another key aspect of this project is data transformation and modeling. By using tools like dbt, you can create modular SQL transformations, automate schema updates, and build dimensional models that are easy to maintain and scale. Incorporating orchestration tools like Apache Airflow adds another layer of expertise, showing your ability to schedule workflows, monitor pipeline performance, and set up automated alerts.
Lastly, such a project underscores operational skills - monitoring system health, ensuring data quality, and scaling resources to meet production demands. These hands-on, practical skills are exactly what hiring managers value in a competitive data engineering portfolio.
How do observability tools like Monte Carlo improve the reliability of data pipelines?
Observability tools like Monte Carlo turn data pipelines from unpredictable "black boxes" into systems you can fully monitor and understand. By keeping tabs on lineage, schema changes, and data quality metrics, these tools can spot anomalies in real-time - things like missing rows, unexpected null values, or metric drift. This means engineers can tackle problems right away, keeping downstream analytics running smoothly and meeting SLAs without a hitch.
Monte Carlo also offers complete visibility across the entire data stack, connecting data sources to dashboards. With features like lineage graphs and automated quality checks, engineers can confidently validate changes and sidestep hidden bugs. This forward-thinking approach not only boosts pipeline reliability but also showcases the kind of advanced skills and attention to detail that stand out in portfolio projects and impress hiring managers.
What are the benefits of using AWS S3 and Redshift to build a data lake for large-scale analytics?
Using AWS S3 to create a data lake offers highly scalable, durable, and affordable storage, making it perfect for managing massive amounts of data. When you integrate it with Amazon Redshift, you unlock the capability to run fast, scalable SQL analytics, allowing you to process large workloads efficiently.
Together, these tools deliver a secure and adaptable architecture that can effortlessly scale with your needs. This makes it a smart choice for tackling complex analytics while keeping costs under control.
