5 Tools To Showcase Data Engineering Skills
In 2026, standing out as a data engineer requires more than just listing skills like SQL or Python. Employers want proof you can handle complex workflows, optimize systems, and solve real problems. Five tools that can elevate your portfolio are Apache Airflow, AWS, Snowflake, dbt, and Apache Spark. Each tool demonstrates expertise in critical areas like pipeline orchestration, cloud infrastructure, data warehousing, transformations, and large-scale data processing.
Here’s a quick summary of how these tools can boost your portfolio:
- Apache Airflow: Showcases workflow orchestration using Python, task dependencies, and production-ready pipelines.
- AWS: Highlights cloud-based pipeline design, cost-efficient storage, and serverless automation.
- Snowflake: Demonstrates modern data warehousing with features like Snowpark, Dynamic Tables, and AI-ready integrations.
- dbt: Adds SQL transformation with software engineering principles, automated testing, and modular design.
- Apache Spark: Proves capability in big data processing, streaming analytics, and machine learning at scale.
Mastering these tools and building end-to-end projects can help you stand out in a competitive job market. Below, we’ll explore how each tool works, its industry relevance, and key features for data engineering.
1. Apache Airflow
Portfolio Relevance
Apache Airflow allows you to define data pipelines using Python code, showcasing your ability to implement software engineering practices like version control and modularity. By building an Airflow DAG, you demonstrate expertise in managing complex task dependencies and delivering workflows ready for production. For instance, you could design a pipeline that extracts data from an API, loads it into Snowflake, applies dbt transformations, and sends a Slack notification - all seamlessly orchestrated in one workflow.
Industry Adoption in 2026
With over 30 million monthly downloads, Apache Airflow has established itself as the go-to open-source tool for orchestrating ETL/ELT pipelines. According to an Apache Airflow survey, 90% of users rely on it specifically for ETL/ELT processes that drive analytics. This widespread usage cements Airflow as a must-know tool for data engineers.
"Apache Airflow is the industry-standard workflow orchestrator for data engineering. It lets you define pipelines as Python code, schedule them, set dependencies, and monitor execution in a clean UI." – The Data Forge
Recent updates, such as Airflow 3.1.0 (released in September 2025) and airflowctl 0.1.0 (introduced in October 2025), have prioritized usability improvements and secure, API-driven control.
Core Features for Data Engineering
Airflow's TaskFlow API makes pipeline creation more straightforward by using Python decorators like @task, which automatically handle data passing between tasks. Its web UI provides real-time insights into task statuses, logs, and durations, making troubleshooting more efficient. Additionally, Airflow supports data-driven scheduling through "Datasets", enabling DAGs to trigger based on updates to specific data objects instead of relying solely on time-based schedules.
Beyond traditional ETL tasks, Airflow is also used for emerging fields - 23% of users employ it for MLOps, while 9% use it for Generative AI workflows. This highlights its adaptability to various use cases.
Scalability and Integration Capabilities
Airflow's modular setup - which includes a Scheduler, Executor, Workers, and a Metadata Database - ensures it can scale effortlessly to accommodate increasing workloads. For large-scale operations, the KubernetesExecutor enables auto-scaling in response to demand.
Additionally, Airflow supports over 100 pre-built operators, making it easy to integrate with major cloud platforms and tools like AWS, Snowflake, dbt, Databricks, and Spark. This broad compatibility creates a unified orchestration layer, giving you the flexibility to explore and incorporate other tools into your data engineering toolkit.
sbb-itb-61a6e59
2. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Portfolio Relevance
In the competitive job market, showcasing expertise in AWS can set you apart by demonstrating your ability to design and manage complete data pipelines. A portfolio project featuring AWS can highlight skills like orchestrating data ingestion with tools such as Kinesis or AppFlow, managing storage with Amazon S3 or Redshift, and automating workflows using AWS Step Functions or Amazon Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (MWAA). For example, building a Lake House architecture - where a central data lake integrates with specialized data stores - proves you can unify analytics platforms and eliminate data silos.
Projects that incorporate AWS serverless tools, like AWS Glue and Lambda, emphasize your ability to create cost-efficient, scalable systems. For instance, implementing S3 Lifecycle policies to transition data from S3 Standard to S3 Glacier demonstrates financial management skills. Similarly, using Lambda for quick tasks under its 15-minute execution limit, while leveraging Glue for more resource-heavy ETL processes, reflects a strong grasp of system design and optimization. These hands-on projects not only enhance your skills but also mirror the practical applications outlined below.
Industry Adoption in 2026
AWS continues to serve as the backbone of modern data infrastructure, offering both performance and cost advantages. Companies like Merck and Vyaire Medical have reported cost savings of up to 50% by moving legacy processes to AWS Glue.
"AWS Glue automatically scales even the most demanding resource-intensive data processing jobs from gigabytes to petabytes with no infrastructure to manage." – AWS Product Documentation
With advancements like zero-ETL integrations, AWS now enables near real-time data movement from operational databases like Aurora and MySQL directly into Redshift, eliminating the need for manual pipeline setups. In February 2026, AWS Glue introduced a REST-based connector that integrates seamlessly with any REST-enabled data source, removing the need for custom libraries.
Core Features for Data Engineering
AWS Glue plays a pivotal role in data integration, connecting to over 70 data sources and providing a Data Catalog with free storage for the first million objects [19, 24]. New features, such as Amazon Q Data Integration and automated Spark upgrade agents, simplify ETL job creation and speed up migrations.
Another recent addition, Amazon S3 Tables, optimizes storage for analytics workloads by using Apache Iceberg open table formats. For workflow orchestration, MWAA supports complex Python-based workflows, while Step Functions offers a low-code option with built-in state management and checkpoints. These tools enhance portfolio projects by showcasing practical, production-ready engineering skills.
Scalability and Integration Capabilities
AWS services are designed to scale effortlessly, from gigabytes to petabytes, adapting to the demands of any project. For instance, AWS Glue dynamically provisions workers based on workload requirements. Enhancements like Amazon EMR's Apache Spark upgrade agent simplify version migrations across clusters, while AWS Glue Flex reduces costs by up to 35% for non-urgent workloads, such as testing or pre-production tasks [27, 28].
The platform also supports the "Bronze, Silver, Gold" data modeling approach, which organizes data into raw, cleaned, and aggregated layers within S3-based data lakes. Features like CloudWatch logs and SNS alerts ensure robust monitoring, secure data practices, and automated pipeline recovery, demonstrating readiness for production environments. Combined with AWS Glue's pay-as-you-go pricing - billed per second with a 1-minute minimum - and Lambda's pay-per-use model, these tools enable cost-effective, scalable systems that can elevate any data engineering portfolio.
3. Snowflake
Portfolio Relevance
Snowflake brings a modern touch to data engineering portfolios, offering tools that highlight your expertise in ZeroOps engineering. With Snowflake, you can create projects that focus on pipeline logic and data quality, showcasing features like Snowpark for Python-driven transformations, Dynamic Tables for declarative data modeling, or Apache Iceberg for open lakehouse architectures.
For example, a project using a Git-integrated Snowflake Notebook can demonstrate version-controlled workflows in Python and SQL. Similarly, leveraging Snowflake Cortex's LLM functions for tasks like sentiment analysis or text summarization within data pipelines can illustrate AI-ready capabilities - all without requiring data relocation.
What sets Snowflake apart is its declarative model, which shifts your focus to data strategy rather than infrastructure maintenance. For instance, using Dynamic Tables to replace traditional orchestration DAGs shows your grasp of modern approaches, where you define the desired outcomes and let Snowflake manage the refresh logic seamlessly.
Industry Adoption in 2026
Snowflake continues to gain traction among enterprises, thanks to its cost efficiency and performance. Companies like Pfizer achieved a 57% reduction in total cost of ownership (TCO) while processing data four times faster. Bond Brand Loyalty cut costs by 50% after transitioning their daily transaction processing from managed Spark to Snowflake.
Travelpass, a travel company, reported 65% cost savings and successfully deployed 130 Dynamic Tables in just one week after switching from a competing platform.
"Now with fewer ephemeral failures and higher visibility in Snowflake, we have a platform that's much easier and cost-effective to operate than managed Spark." – David Trumbell, Head of Data Engineering, CTC
These examples highlight how Snowflake helps businesses streamline operations and reduce costs, making it a sought-after platform in the data engineering space.
Core Features for Data Engineering
Snowflake offers a suite of features tailored for modern data engineering:
- Snowpark: Enables complex transformations in Python, Java, or Scala without moving data.
- Dynamic Tables: Automates data refreshes and dependency management based on freshness targets, simplifying orchestration.
- dbt Integration: Brings modularity and CI/CD practices into SQL workflows via the Snowsight UI.
- Apache Iceberg Support: Delivers interoperability with external tools while maintaining Snowflake's strong performance and governance.
- Snowflake Marketplace: Provides ready access to third-party datasets, eliminating the need for custom ingestion pipelines.
The platform's pricing model is straightforward: compute is billed only when virtual warehouses are active, and storage costs are based on average monthly usage. These features make it easy to build scalable, enterprise-ready architectures.
Scalability and Integration Capabilities
Snowflake’s architecture, which separates storage from compute, allows resources to scale independently to meet workload demands. This design supports massive parallel processing and eliminates the need for manual cluster management. Features like Snowflake Openflow enable seamless integration across structured and unstructured data sources.
For monitoring and reliability, Snowflake Trail offers built-in telemetry, logging, and alerting - tools that demonstrate robust pipeline management. The Snowflake Python API adds another layer of functionality, allowing programmatic control over databases, schemas, and tasks. This capability showcases advanced automation skills, extending beyond basic SQL workflows.
With unified governance and consistent performance across cloud platforms, Snowflake equips you to build sophisticated, production-ready data systems that can handle enterprise-level challenges with ease.
4. dbt (Data Build Tool)
Portfolio Relevance
dbt adds a unique edge to a data engineering portfolio by focusing on transformation logic and modular design. It brings software engineering principles into SQL-based transformations, showcasing skills like version control, automated testing, and CI/CD practices. These elements signal to recruiters that you’re not just proficient in SQL but also understand modern development workflows.
The tool’s automated documentation and lineage graphs make it easy for hiring managers to explore your data models and trace how raw data transforms into actionable business metrics. A layered modeling approach - organizing data into staging, intermediate, and mart layers - demonstrates a structured and professional data architecture. For instance, a retail analytics team used dbt to create layered models in AWS Redshift, boosting data accessibility and cutting costs. Using the ref function to build dependency graphs further highlights your ability to follow best practices.
Industry Adoption in 2026
By 2026, dbt has firmly established itself with over 100,000 community members. Companies report a 194% ROI within six months of adoption, with automated workflows speeding up processes by as much as 30×.
The tool holds a 4.8/5 rating on G2, with 97% of data leaders expressing satisfaction. Senior Data Engineer Kelly Wolinetz from M1 Finance praised dbt and its Semantic Layer for enhancing AI-driven investments, stating:
"For our business needs, our investment in AI and dbt Semantic Layer has been worth it."
– Kelly Wolinetz, Senior Data Engineer, M1 Finance
Similarly, WHOOP’s Senior Director of Analytics, Matt Luizzi, leveraged dbt to deliver precise, customer-critical data. The February 2026 announcement of dbt Labs’ agreement with Fivetran further signaled the growing trend of unified data ingestion and transformation platforms, making dbt expertise even more valuable.
Core Features for Data Engineering
dbt simplifies complex SQL operations by enabling modular SELECT statements. Instead of manually creating tables and views, you define the desired output, and dbt handles the rest.
Its Jinja templating and macros help reduce redundant code, adhering to the "Don't Repeat Yourself" principle. Built-in testing features - like schema validations (e.g., unique, not null) and custom logic tests - ensure data quality before it reaches production dashboards. Open-source packages like dbt-utils further enhance functionality, offering tools for dependency management and standardized logic.
The dbt Semantic Layer allows you to define metrics once and use them consistently across BI dashboards and AI tools. New for 2026, dbt Copilot automates code, documentation, and test generation, while the Fusion engine streamlines development and optimizes costs.
Scalability and Integration Capabilities
dbt integrates seamlessly with major cloud platforms like Snowflake, BigQuery, Databricks, and Redshift, preparing you to work with the modern data stack. Its dbt Mesh framework supports scalability by enabling teams to share and manage data assets across projects through cross-project references.
For orchestration, dbt works well with Apache Airflow, offering hooks, operators (e.g., DbtCloudRunJobOperator), and sensors to manage dbt jobs within Airflow workflows. This separation of orchestration (Airflow) and transformation (dbt) ensures smooth collaboration between data engineering and analytics teams.
Incremental materializations in dbt process only new or updated data, cutting compute costs and speeding up pipelines - key for large-scale data warehouses. With over 700 connectors via Fivetran and support for Snowflake Cortex AI functions, dbt allows you to integrate tasks like sentiment analysis or text classification directly into pipelines. This compatibility with orchestration tools like Airflow cements dbt’s importance in today’s data workflows.
5. Apache Spark
Portfolio Relevance
Apache Spark is a standout addition to your portfolio, offering a unified platform for batch processing, streaming analytics, SQL, and machine learning. Its high-level APIs - available in Python, SQL, Scala, Java, and R - make it easier to create clear, impactful projects that catch the eye of hiring managers. Thanks to its in-memory processing capabilities, Spark can be up to 100× faster than Hadoop MapReduce when caching data, and 10× faster when reading from disk. A great way to showcase your expertise is by building a Structured Streaming project that ingests Kafka data into a Delta Lake table or creating an ETL pipeline using Spark SQL and MLlib. This versatility and speed are key reasons why Spark has become a go-to tool for major companies.
Industry Adoption in 2026
By February 2026, 80% of Fortune 500 companies will be using Apache Spark to power their big data operations. Its ability to scale is unmatched, demonstrated by its support for clusters with up to 8,000 nodes and the capacity to process data on a petabyte scale. Recent advancements, like the preview of Spark 4.2.0 on February 8, 2026, and the stable release of Spark 4.0.2 just days earlier, highlight its ongoing development with contributions from over 2,000 developers across industry and academia. The rise of serverless Spark options from leading cloud providers has further simplified its use, enabling engineers to focus on creating efficient data pipelines. As Matei Zaharia, VP of Apache Spark and Co-founder of Databricks, explained:
"At Databricks, we're working hard to make Spark easier to use and run than ever... All of our work on Spark is open source and goes directly to Apache."
Core Features for Data Engineering
Apache Spark’s architecture is packed with features tailored for data engineering. Spark SQL provides a distributed engine for structured data queries, while Structured Streaming supports near real-time, fault-tolerant processing. For machine learning tasks like classification and regression, MLlib offers scalable solutions, and GraphX handles graph-parallel computations. These components are built on Spark Core, which manages essential tasks like memory allocation, I/O, and scheduling. Modern enhancements like Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) can accelerate TPC-DS queries by up to 8× by optimizing joins and shuffles. Additionally, Spark Connect, introduced in version 3.4, allows developers to work locally in IDEs like PyCharm or VS Code while running heavy computations on remote clusters. In 2026, the introduction of Spark Declarative Pipelines (SDP) makes development even more intuitive by letting engineers focus on defining data flows rather than managing the mechanics.
Scalability and Integration Capabilities
Apache Spark’s strength lies in its seamless integration with a wide range of tools and systems. It connects effortlessly with storage solutions like Amazon S3, HDFS, and MongoDB, orchestration tools like Airflow, and BI platforms such as Tableau and Power BI. Its deep compatibility with Lakehouse architectures, particularly with Delta Lake and Apache Iceberg, brings ACID transactions to data lakes, combining the flexibility of a data lake with the reliability of a data warehouse. Spark’s unified DataFrame API allows users to handle both real-time and historical data analysis using the same approach. With over 43% of organizations running Spark workloads in the cloud using services like AWS EMR and Google Dataproc, and support for both x86_64 and ARM64 architectures, mastering Spark through a data engineering and AI academy equips you to tackle enterprise-level data challenges with confidence.
How to Build Your Data Engineering Portfolio
Many aspiring engineers use structured programs like the DataExpert.io Academy to build these high-quality projects.
Tool Comparison Table
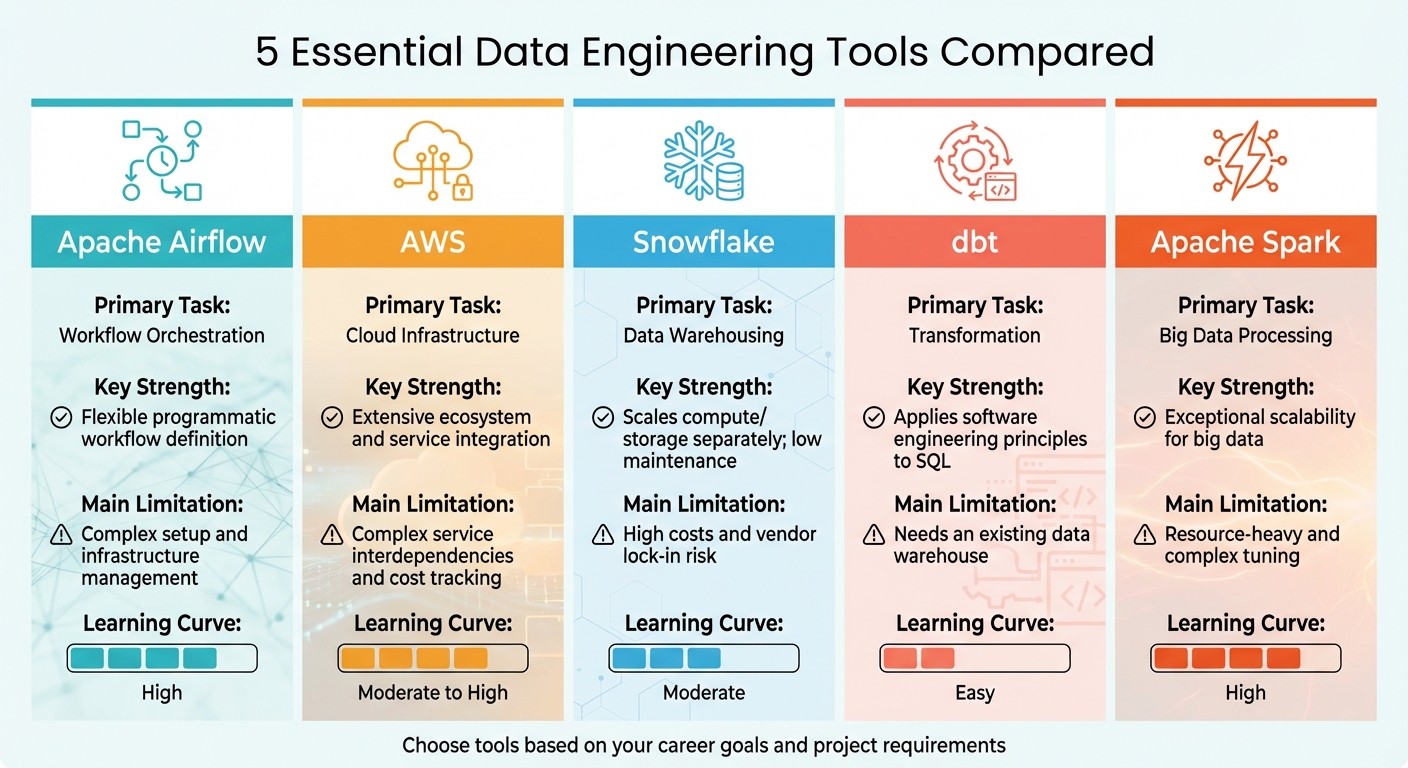
Data Engineering Tools Comparison: Airflow, AWS, Snowflake, dbt, and Spark
Choosing the right tools depends on your career aspirations and project needs. Each of the five tools discussed in this article plays a unique role in the data engineering process. By understanding their strengths, limitations, and learning curves, you can better decide which ones to prioritize for mastering.
The table below provides a snapshot of each tool's primary function, what it excels at, its drawbacks, and how challenging it is to learn. For example, Apache Airflow shines in workflow orchestration but requires significant DevOps expertise. On the other hand, Snowflake simplifies data warehousing with minimal maintenance but comes with the risk of vendor lock-in. dbt is user-friendly and follows software engineering principles but relies on an existing data warehouse. Meanwhile, AWS offers an extensive ecosystem, and Apache Spark is ideal for large-scale data processing, though it has a steep learning curve.
| Tool | Primary Task | Key Strength | Main Limitation | Learning Curve |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apache Airflow | Workflow Orchestration | Flexible programmatic workflow definition | Complex setup and infrastructure management | High |
| AWS | Cloud Infrastructure | Extensive ecosystem and service integration | Complex service interdependencies and cost tracking | Moderate to High |
| Snowflake | Data Warehousing | Scales compute/storage separately; low maintenance | High costs and vendor lock-in risk | Moderate |
| dbt | Transformation | Applies software engineering principles to SQL | Needs an existing data warehouse | Easy |
| Apache Spark | Big Data Processing | Exceptional scalability for big data | Resource-heavy and complex tuning | High |
This comparison is designed to help you map out which tools align best with your immediate goals and long-term career plans. Whether you're aiming for ease of use or scalability, understanding these trade-offs can guide your learning journey effectively.
Conclusion
Mastering tools like Apache Airflow, AWS, Snowflake, dbt, and Apache Spark demonstrates your readiness to tackle complex data challenges. As Zach Wilson, Founder of DataExpert.io, aptly put it, "A portfolio piece shouldn't be easy to create". These tools are central to modern data infrastructure, and showcasing your practical expertise through portfolio projects can set you apart from candidates with only theoretical knowledge.
The key to landing interviews often lies in presenting demonstrable skills. Earlier sections emphasized how end-to-end projects - featuring pipeline building, incremental data loading, and medallion architecture - help top candidates stand out.
These tools enable you to craft a portfolio that mirrors the challenges of real-world data systems. DataExpert.io Academy offers structured, hands-on training to help you develop these skills. With free cloud access to platforms like Databricks, AWS, Snowflake, and Astronomer (Airflow), students can create production-ready projects that run for months, not days. Backed by over 250 hours of practical content and a 4.9/5 Trustpilot rating, the academy focuses on teaching actionable skills.
Capstone projects take this training even further, allowing students to apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios like real-time Formula 1 analytics, cryptocurrency trading strategies, and sports betting applications. As Mitali Gupta, a student, shared:
"One of the most rewarding aspects of the bootcamp was the ability to immediately apply the knowledge gained. The techniques and strategies taught by Zach have already proven effective in my day-to-day work."
FAQs
Which tool should I learn first?
When deciding where to begin, it all comes down to your goals and level of experience. If you're just starting out, Apache Airflow is a great choice. It's a popular tool for managing data pipelines and automating workflows, making it a solid foundation for beginners.
If you're looking to broaden your skill set, consider diving into AWS for cloud services or Snowflake for data warehousing. Starting with Airflow helps you build essential workflow management skills, while tools like AWS and Snowflake allow you to expand your knowledge as you gain more experience.
What’s a strong end-to-end portfolio project using these tools?
A well-rounded portfolio project can highlight your data engineering skills by building a fully functional data pipeline from start to finish. For instance, you could start by extracting data from APIs or flat files and storing it in Amazon S3. From there, load the data into Snowflake and apply transformations using tools like DBT or Airflow.
To make your project stand out, incorporate features such as incremental data loads, metadata-driven pipelines, and automation. These elements showcase your ability to handle data ingestion, transformation, and workflow orchestration - key skills that employers look for in the field.
How can I prove production-ready skills, not just tutorials?
To truly demonstrate your skills, build real-world data pipelines and projects that tackle challenges professionals face every day. This means working with messy, unstructured data, designing scalable architectures, and incorporating data quality checks to ensure reliability. Use tools like Airflow, Snowflake, and AWS to create workflows that are not just functional but ready for deployment in production environments.
The key is to deliver end-to-end solutions. Go beyond following basic tutorials - showcase your ability to implement best practices, optimize performance, and solve complex problems. This approach highlights your readiness to handle real-world scenarios and adds depth to your portfolio.
