
Case Study: Optimizing Analytics with dbt and Snowflake
Here’s the problem: Legacy analytics systems were slow, unreliable, and hard to manage. Teams wasted hours fixing errors, dealing with incomplete data, and untangling poorly structured systems. These inefficiencies drained resources and delayed insights.
The solution? dbt and Snowflake. Together, they transformed how companies like Reforge, JetBlue, and others processed data. By combining dbt’s version control, automated testing, and modular SQL modeling with Snowflake’s scalable cloud architecture, teams achieved faster workflows, reduced costs, and improved data quality.
What changed:
- Faster processing: Query times dropped dramatically (e.g., 6 hours to 9 minutes for one workflow).
- Saved time: Teams reclaimed up to 18 hours of work weekly by automating tasks.
- Lower costs: Smarter resource allocation cut expenses by thousands annually.
- New capabilities: Tools like data lineage, real-time monitoring, and AI-powered analytics became accessible.
This article explains how organizations built a structured, three-layer data pipeline using dbt and Snowflake, tackled technical challenges, and achieved measurable results. If you’re stuck with outdated systems, this guide offers practical steps to modernize your analytics stack.
Business Problems and Starting Point
Legacy System Limitations
Before tools like dbt and Snowflake entered the picture, analytics systems struggled to keep pace with modern data needs. Take the case of a global technology company's marketing team: their primary data workflows, running on Alteryx and an on-premises SQL Server, required a staggering 6 hours daily to process. The outdated tools lacked modularity and version control, meaning every data run required reprocessing everything from scratch - a time-consuming and inefficient process.
Knichel Logistics, a transportation company based in the U.S., faced its own set of challenges. Their system consisted of over 460 tables scattered across their infrastructure, with no naming conventions or documentation to guide them. This chaotic setup, which they called "Architecture Anarchy", made managing data a nightmare. Without frameworks for automated validation, data reliability became a guessing game, and inefficient full table refreshes significantly increased Snowflake costs.
Beyond these specific cases, the broader problem with legacy systems was their drain on resources. They consumed up to 70% of IT budgets, with teams spending over 16 hours a week just patching outdated software. Data silos added another layer of complexity, stifling collaboration between departments. Meanwhile, businesses were drowning in unstructured data, which was growing at a rate of 61% annually. Yet, 54% of corporate data sat unused and stale, offering no value.
These limitations didn’t just strain infrastructure - they actively disrupted the ability to function effectively on a daily basis.
Effects on Daily Operations
The technical shortcomings of legacy systems had a direct and frustrating impact on daily workflows. For instance, at the same global technology company, analysts had to manually coordinate interdependent workflows. If they started processes too soon, the data would be incomplete. Worse, overnight errors often led to failures that carried over into the next day, creating a ripple effect of delays and inefficiencies.
"If there was an error the night before, the data would be incorrect or out of date... analysts could focus on what they do best: getting insights from the data and generating value from them." - Indicium Tech
Another major issue was the time analysts spent untangling data lineage. They had to figure out how changes in one column would affect downstream models, pulling them away from their primary goal of extracting insights. At dbt Labs, for example, their internal analytics team faced a bottleneck when an unoptimized model processing 5 billion records took 1.5 hours to run. This single task consumed half of their 3-hour processing window and added $1,800 per month in compute costs. The inefficiency meant they could only refresh data four times a day, leaving users with outdated information for long stretches of time.
These operational hurdles made it clear that legacy systems weren’t just outdated - they were actively holding businesses back.
Building the Solution with dbt and Snowflake
3-Layer Data Pipeline Structure
To address inefficiencies in legacy systems, the team implemented a structured three-layer data pipeline. The Staging layer served as the entry point, where raw data was ingested using dbt's source function. This layer mirrored the structure of the source tables and applied basic standardizations.
Next came the Intermediate layer, which combined staging models and performed initial transformations. For instance, in a December 2025 trading profit and loss project led by Dmytro Yaroshenko from Snowflake and Luis Leon from dbt Labs, this layer integrated trading history with foreign exchange rates sourced directly from the Snowflake Marketplace. Finally, the Marts (Analytics) layer acted as the output destination, consolidating advanced business logic. This layer was often subdivided into folders like core for key business metrics, aggregates for BI dashboards, and ml for machine learning features.
The entire architecture relied on a declarative approach, simplifying pipeline management and reducing development time compared to imperative workflows.
"Because dbt uses a declarative vs. an imperative model, you save a lot of time in building declarative models versus imperative workflows." – Luis Leon, Analytics Engineer at dbt Labs
This layered approach provided a strong foundation for leveraging advanced technical capabilities.
Technical Features Used
The solution incorporated several advanced features to enhance efficiency and scalability:
- Modular SQL modeling: Transformations were reusable and version-controlled, making them easy to manage across environments. Developers could dynamically switch materialization strategies - using views for rapid prototyping and transitioning to tables or incremental materializations in production for better performance.
- Snowflake Dynamic Tables: These tables automated incremental updates while enabling warehouse-level scalability, optimizing costs. For example, in the trading project, Dynamic Tables handled multi-currency trade normalization and automatically compared actual performance against portfolio targets.
-
Snowflake Cortex LLM functions: Integrated directly into dbt models, these functions added advanced capabilities. In the trading project, the
int_extracted_entities.sqlmodel usedSNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.SENTIMENTandCLASSIFY_TEXTto extract market signals from trader notes - without moving data outside the warehouse. - Snowflake Marketplace integration: Teams could seamlessly join internal data with external datasets, such as FX rates and stock prices, with zero ETL latency and no additional storage costs.
Implementation Steps and Tools
The team followed a streamlined process, leveraging integrated tools to build the solution. Snowflake's Git integration and the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE FROM command allowed them to run setup scripts directly from a repository. Using Jinja templating, they dynamically created development, staging, and production environments from the same codebase. The CREATE OR ALTER command further simplified environment management by auto-generating the necessary DDL commands.
For the trading profit and loss project, the team:
- Configured a
profiles.ymlfile with separate dev and prod targets, using a GitHub Personal Access Token for seamless version control. - Onboarded FX rates and US equity price history directly from the Snowflake Marketplace.
- Loaded target allocation ratios via CSV files using
dbt seed. - Executed transformations across all three pipeline layers using
dbt run, with Snowflake automatically managing compute resources.
"dbt allows you to focus on the content of your data products, while the framework takes care of generating the DDL to deploy them with various materialization options." – Dmytro Yaroshenko, Data Engineer, Snowflake
The solution also emphasized granular compute control, enabling teams to allocate warehouse sizes at the model level. This ensured resources were scaled appropriately - minimizing waste on smaller tasks while allocating sufficient power to heavier workloads. By combining dbt's transformation framework with Snowflake's AI Data Cloud, the team built a streamlined pipeline capable of delivering advanced analytics with minimal overhead.
Building Data Marts with dbt + Snowflake
sbb-itb-61a6e59
Results and Business Impact
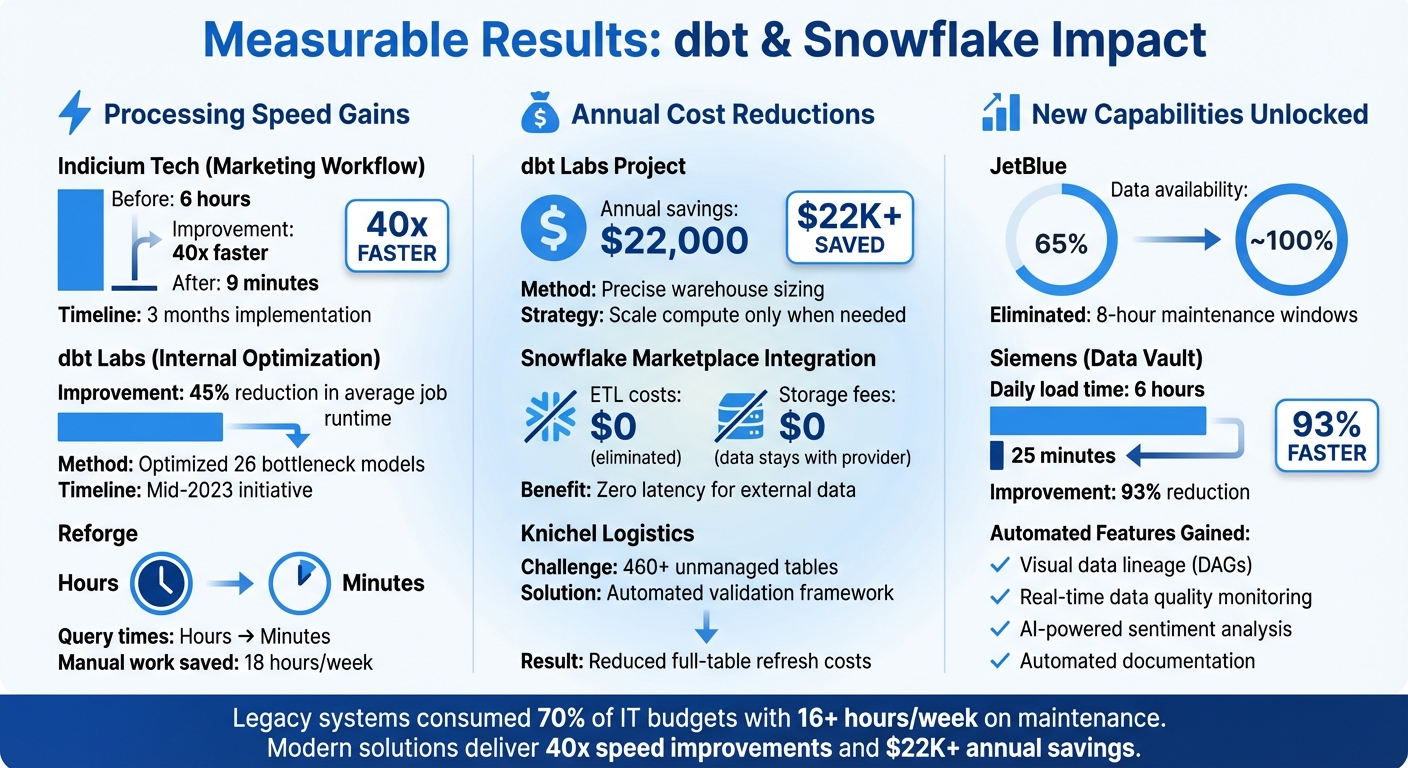
dbt and Snowflake Analytics Optimization Results: Performance and Cost Improvements
Performance Improvements
The migration delivered a massive boost in processing times across various projects. Indicium Tech saw a marketing workflow's runtime drop from over 6 hours to just 9 minutes - a stunning 40x improvement. This transformation was achieved over three months by refactoring numerous interconnected Alteryx workflows into dbt models operating on Snowflake. The audit_helper package ensured seamless data compatibility throughout the process.
At dbt Labs, Senior Data Engineer Elize Papineau spearheaded an optimization initiative in mid-2023 to address performance issues without altering a single model. By examining Snowflake query tags and metadata views, the team pinpointed 26 bottleneck models and fine-tuned warehouse sizing. The result? A 45% reduction in average dbt Cloud job runtime. Similarly, Reforge experienced a dramatic improvement in query speeds after transitioning from Postgres to Snowflake and dbt.
These advancements not only accelerated workflows but also unlocked meaningful cost savings and expanded capabilities.
Cost and Resource Savings
Optimized architectures brought significant cost efficiencies through smarter resource allocation. For instance, dbt Labs' internal project saved approximately $22,000 annually, even while using larger warehouse instances for specific high-demand tasks. The secret? Implementing precise recommendations to scale compute resources only when the performance benefits were guaranteed.
"Underperforming models were flagged for refactoring, maximizing human time." – Elize Papineau, Sr. Data Engineer, dbt Labs
Reforge also reaped time savings, cutting 18 hours of manual work each week by eliminating the need for constant resource management. Additionally, using the Snowflake Marketplace removed ETL costs for external data sources like FX rates and stock prices, as the data stayed on the provider's side, incurring no extra storage fees.
But the benefits didn’t stop at cutting costs - teams also gained access to new tools and capabilities that were previously out of reach.
New Capabilities Gained
Teams unlocked automated data lineage and documentation through dbt’s visual DAGs, making it much easier to identify dependencies and troubleshoot errors compared to manual methods. At Reforge, Head of Data Daniel Wolchonok introduced Metaplane for automated data observability, enabling the team to catch quality issues, such as distribution drift or missing data, in real time.
"Because of Metaplane, I spook people with how quickly I find data issues now. I know when events are created with crappy names, when there are new attributes... It helps me catch issues that are painful to untangle." – Daniel Wolchonok, Head of Data, Reforge
The integration of AI-powered analytics via Snowflake Cortex added another layer of capability. Teams could now analyze unstructured trader notes for market signals and sentiment directly within their transformation workflows using LLM functions - all without moving data outside the warehouse. This declarative approach democratized data transformation, empowering anyone with SQL knowledge to build production-ready pipelines, which reduced dependency on specialized data engineers.
These advancements not only improved performance and reduced costs but also set the stage for future innovations and best practices in analytics workflows.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
What Worked Well
The declarative approach played a key role for teams combining dbt with Snowflake. Instead of relying on intricate imperative scripts, they could simply define the desired state of their data models and allow the platforms to handle the execution. This shift opened the door for a broader range of contributors - anyone familiar with SQL could now build production-ready pipelines. For example, Siemens saw this in action when IT Business Partner Rebecca Funk spearheaded their standardized Data Vault implementation. The team collaborated effortlessly on the same Snowflake project without worrying about infrastructure setup. Features like built-in testing and straightforward job scheduling enabled them to focus on solving business challenges immediately, which led to a 93% reduction in daily load times - from 6 hours to just 25 minutes.
The 3-layer modeling structure also stood out, creating clear boundaries that made projects easier to both manage and scale. Teams took advantage of dynamic warehouse resizing at the model level, scaling up for heavy transformations and scaling down right after to control costs. These strategies laid the groundwork for addressing future challenges with precision.
Problems Encountered and Solutions
While there were plenty of wins, a few technical hurdles emerged during implementation.
Non-deterministic functions posed an issue. For instance, when a trading analytics team used Snowflake Cortex LLM functions in dbt models to analyze sentiment from trader notes, their Dynamic Tables couldn’t refresh incrementally. The fix? Overriding the project-level incremental settings with refresh_mode=full specifically for models using these functions.
External dependency access was another challenge. dbt projects often require packages from dbt Hub or GitHub, but Snowflake’s default security settings block these connections. Teams addressed this by setting up Snowflake Network Rules and External Access Integrations to securely allow egress to specific URLs.
Environment inconsistency between development and production environments led to configuration drift for some teams. The solution involved using Jinja macros along with Snowflake's CREATE OR ALTER construct. This approach enabled declarative, template-based environment setup, eliminating manual errors and ensuring more reliable deployments.
Advice for Similar Projects
Drawing from these experiences, here are some practical tips for similar initiatives:
- Start with views for rapid prototyping before transitioning to tables or incremental materialization. This keeps development fast while avoiding unnecessary compute costs until multiple users need access to the same objects. Dynamic warehouse resizing at the model level ensures resources are scaled appropriately for each workload.
-
For monitoring and troubleshooting, enable detailed logging by setting
LOG_LEVEL = 'INFO',TRACE_LEVEL = 'ALWAYS', andMETRIC_LEVEL = 'ALL'on schemas where dbt objects are deployed. This setup captures execution metrics that can quickly highlight performance bottlenecks. -
The Tasty Bytes implementation provided a great example of using dedicated warehouses for dbt workloads. They created a dedicated
TASTY_BYTES_DBT_WH(XLARGE) for materializing complex models and scheduled execution via Snowflake Tasks. This simplified their tech stack and reduced orchestration challenges. Usedbt seedfor version-controlled static data. - Take advantage of the Snowflake Marketplace for external data sources. This eliminates ETL latency and storage costs since the data stays on the provider’s side. Teams needing FX rates and stock prices found this approach particularly effective.
Conclusion
The pairing of dbt and Snowflake is proving to be a game-changer for organizations looking to modernize their analytics workflows. Take JetBlue, for instance - they boosted data availability from 65% to nearly 100% by eliminating the cumbersome 8-hour maintenance windows that plagued their older systems. Similarly, Reforge cut query times from hours to minutes and reclaimed 18 hours of manual work per week.
The key to these successes lies in a well-structured, three-layer data pipeline - staging, intermediate, and marts - that supports scalable and reliable analytics. As Ben Singleton from JetBlue put it:
"The new workflow with dbt and Snowflake isn't a small improvement. It's a complete redesign of our entire approach to data that will establish a new strategic foundation for analysts".
What makes this combination so effective is how it brings software engineering practices into the analytics realm. Features like version control, CI/CD pipelines, and automated documentation empower SQL-savvy team members to create production-ready data models without adding bottlenecks.
Beyond transformation, organizations are seeing cost and performance benefits. Incremental processing and dynamic warehouse sizing help optimize compute costs while handling larger datasets. And since the declarative approach reduces time spent managing infrastructure, teams can focus on delivering actionable insights. This streamlined workflow sets a new benchmark for tackling the challenges that once bogged down legacy systems, enabling businesses to innovate and grow.
For those still using outdated systems, the roadmap is straightforward: start small with a proof of concept, use automated testing to maintain data consistency, and scale up gradually. By combining dbt's transformation tools with Snowflake's elastic architecture, organizations can achieve the scalability and reliability today’s analytics demands.
FAQs
How does a three-layer data pipeline enhance data processing efficiency?
A three-layer data pipeline brings a structured and modular approach to managing data workflows, making processes more efficient and scalable. By breaking tasks into layers, it supports incremental data loading, reduces bottlenecks, and simplifies how data transformations are handled.
In a case study, tools such as dbt and Snowflake showcased how this pipeline setup can improve analytics workflows. This design not only keeps performance steady as data demands grow but also ensures everything stays organized and manageable.
What are the key advantages of using dbt with Snowflake for analytics?
Combining dbt with Snowflake simplifies analytics workflows by creating scalable and efficient data pipelines. With dbt, teams can craft modular, version-controlled SQL transformations while sticking to best practices. These transformations integrate seamlessly with Snowflake’s robust cloud platform, making it easier to develop and maintain high-quality data models.
Snowflake’s flexible architecture, combined with dbt’s automation, optimizes resource usage and enhances query performance. This partnership not only helps manage costs but also promotes teamwork and strengthens data governance through built-in documentation and testing tools. By streamlining complex analytics tasks, this combination delivers quicker, more dependable insights for your business.
What’s the best way for businesses to upgrade from legacy systems to a modern analytics stack using dbt and Snowflake?
To move from legacy systems to a modern analytics stack with dbt and Snowflake, businesses should take a well-organized, step-by-step approach. Begin by transferring your data from older systems - whether they’re on-premises or outdated cloud platforms - to Snowflake, a cloud-based data platform known for its scalability and high performance. Proper planning during this stage is crucial to maintain data accuracy and avoid unnecessary disruptions.
Once your data is securely housed in Snowflake, leverage dbt (Data Build Tool) to simplify data transformations and build modular, easy-to-maintain pipelines. With dbt, teams can apply software development practices like version control and CI/CD workflows to their analytics processes. This shift replaces outdated, manual workflows with efficient and scalable solutions. By incorporating incremental data loads and metadata-driven practices, businesses can streamline operations, cut costs, and stay flexible as data requirements evolve.
Making this transition doesn’t just improve operational efficiency and data quality - it also lays the groundwork for tapping into advanced analytics and AI opportunities down the line.
